Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy reveals a new mechanism based on competitive binding between Tris and protein on a conductive biomimetic polydopamine surface†
Abstract
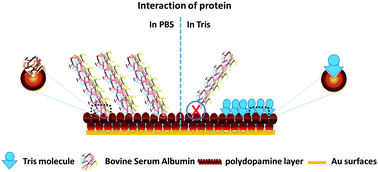
A novel mechanism was developed to study the interaction of mussel inspired polydopamine surfaces with bovine serum albumin using cyclic voltammetry and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy supplemented with XPS, IR spectroscopy, UV spectroscopy and atomic force microscopy. The polydopamine surfaces reveal different mechanisms that give a new insight into understanding the interaction with BSA under the variable conditions used for PDA preparation and BSA adsorption. The study provides an in-depth analysis of the orientations and interactions of BSA with polydopamine surfaces. The protein interaction behavior changed significantly in different environments including different pH values and concentrations of buffer and it revealed a competitive binding mechanism of protein binding. The study provides an outlook for studying the interaction of protein foulants with PDA, which should be carried out in nucleophilic buffers, while the covalent binding or immobilization of biomolecules to PDA surfaces should be carried out in non-nucleophilic buffer for higher efficiency.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...