Structural search for stable Mg–Ca alloys accelerated with a neural network interatomic model†
Abstract
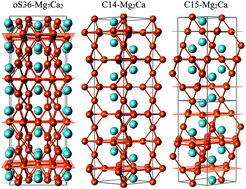
We have combined a neural network formalism with metaheuristic structural global search algorithms to systematically screen the Mg–Ca binary system for new (meta)stable alloys. The combination of these methods allows for an efficient exploration of the potential energy surface beyond the possibility of the traditional searches based on ab initio energy evaluations. The identified pool of low-enthalpy structures was complemented with special quasirandom structures (SQS) at different stoichiometries. In addition to the only Mg–Ca phase known to form under standard synthesis conditions, C14-Mg2Ca, the search has uncovered several candidate materials that could be synthesized under elevated temperatures or pressures. We show that the vibrational entropy lowers the relative free energy of several phases with magnesium kagome layers: C15 and C36 Laves structures at the 2 : 1 composition and an orthorhombic oS36 structure at the 7 : 2 composition. The estimated phase transition temperatures close to the melting point leave open the possibility of synthesizing the predicted materials at high temperatures. At high pressures up to 10 GPa, two new phases at the 1 : 1 and 3 : 1 Mg : Ca stoichiometries become thermodynamically stable and should form in multi-anvil experiments.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...
