Measurement of the surface hydrophobicity of engineered nanoparticles using an atomic force microscope†
Abstract
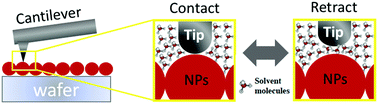
Determination of the surface hydrophobicity or wettability of nanomaterials and nanoparticles (NPs) is often challenged by the heterogeneous properties of NPs that vary with particle size, shape, surface charge, aggregation states, and surface sorption or coating. This study first summarized inherent limitations of the water contact angle, octanol–water partition coefficient (Kow) and surface adsorption of probe molecules in probing nanomaterial hydrophobicity. Then, we demonstrated the principle of a scanning probe method based on atomic force microscopy (AFM) for the local surface hydrophobicity measurement. Specifically, we measured the adhesion forces between functionalized AFM tips and self-assembled monolayers (SAMs) to establish a linear relationship between the adhesion forces and water contact angles based on the continuum thermodynamic approach (CTA). This relationship was used to determine the local surface hydrophobicity of seven different NPs (i.e., TiO2, ZnO, SiO2, CuO, CeO2, α-Fe2O3, and Ag), which agreed well with bulk contact angles of these NPs. Some discrepancies were observed for Fe2O3, CeO2 and SiO2 NPs, probably because of surface hydration and roughness effects. Moreover, the solution pH and ionic strength had negligible effects on the adhesion forces between the AFM tip and MWCNTs or C60, indicating that the hydrophobicity of carbonaceous nanomaterials is not influenced by pH or ionic strength (IS). By contrast, natural organic matter (NOM) appreciably decreased the hydrophobicity of MWCNTs and C60 due to surface coating of hydrophilic NOM. This scanning probe method has been proved to be reliable and robust toward the accurate measurement of the nanoscale hydrophobicity of individual NPs or nanomaterials in liquid environments.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...