Potential models for the simulation of methane adsorption on graphene: development and CCSD(T) benchmarks†
Abstract
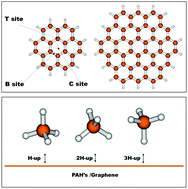
Different force fields for the graphene–CH4 system are proposed including pseudo-atom and full atomistic models. Furthermore, different charge schemes are tested to evaluate the electrostatic interaction for the CH4 dimer. The interaction parameters are optimized by fitting to interaction energies at the DFT level, which were themselves benchmarked against CCSD(T) calculations. The potentials obtained with both the pseudo-atom and full atomistic approaches describe accurately enough the average interaction in the methane dimer as well as in the graphene–methane system. Moreover, the atom–atom potentials also correctly provide the energies associated with different orientations of the molecules. In the atomistic models, charge schemes including small charges allow for the adequate representation of the stability sequence of significant conformations of the methane dimer. Additionally, an intermediate charge of −0.63e on the carbon atom in methane leads to bond energies with errors of ca. 0.07 kcal mol−1 with respect to the CCSD(T) values for the methane dimer. For the graphene–methane interaction, the atom–atom potential model predicts an average interaction energy of 2.89 kcal mol−1, comparable to the experimental interaction energy of 3.00 kcal mol−1. Finally, the presented force fields were used to obtain self-diffusion coefficients that were checked against the experimental value found in the literature. The no-charge and Hirshfeld charge atom–atom models perform extremely well in this respect, while the cheapest potential considered, a pseudo-atom model without charges, still performs reasonably well.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...