Observation of an electric field-induced interface redox reaction and magnetic modification in GdOx/Co thin film by means of depth-resolved X-ray absorption spectroscopy
Abstract
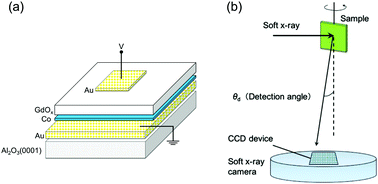
We study an electric field-induced redox reaction at the interface of GdOx/Co thin film, by means of soft X-ray absorption spectroscopy (XAS). The fluorescence-yield depth-resolved XAS analysis reveals that the interfacial Co layer at GdOx/Co is composed of ∼50% Co oxide when the negative field is applied, while metallic Co is dominant in the case of the positive field. We suppose that the interfacial layer is oxidized by oxygen migration from the GdOx layer with the negative field while the interfacial layer shows the metallic state with the positive field, which means that the redox reaction is induced by the electric field. In addition, it is found from the X-ray magnetic circular dichroism (XMCD) measurement that the orbital magnetic moment of Co is larger when the negative electric field is applied to the film, as compared to the positive field. Moreover, the depth-resolved XMCD analysis reveals that the interfacial Co layer shows no or little magnetization regardless of the electric field, while for the inner layer, an increase of the orbital magnetic moment is suggested with the negative field. The field-induced magnetic modification could be attributed to the change of the orbital moment in the inner Co layer due to interfacial modifications. We thus succeed in the direct observation of the redox reaction-induced change in the interface magnetic state.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...