Interplay of entropy and enthalpy in peptide binding to zwitterionic phospholipid membranes as revealed from membrane thinning†
Abstract
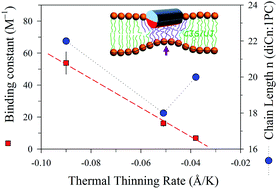
Membrane thinning that resulted from peptide-binding is observed via temperature dependent small-angle X-ray scattering (SAXS). The result reveals a mean thermal thinning rate of 0.038 Å K−1 for the neat unilamellar vesicles (ULVs) of a zwitterionic phospholipid of 1,2-dieicosenoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine (diC20:1PC) in the temperature range of 285–312 K. The thinning effect promotes greatly the association between a model antimicrobial peptide melittin and the ULV. Scaling the observed isothermal melittin–ULV bilayer thinning to that measured using low-angle X-ray diffraction from the melittin–multilamellar membranes of defined peptide-to-lipid ratios establishes temperature-dependent binding isotherms χb of the peptide–ULV as a function of free peptide concentration in solution. From the binding isotherms, temperature-dependent peptide–membrane binding constant K(T) is extracted on the basis of a modified Gouy–Chapman model. Changes in K(T) follow the linearized van’t Hoff equation ln K(T) ∝ −ΔHT−1 with a constant enthalpy change ΔH = 9.6 kcal mol−1, suggesting an entropy-driven binding process prior to membrane pore formation. Correspondingly, a five-fold enhancement of K is observed in the temperature range studied. The peptide-binding strength is found to follow the growth trend of the membrane thermal thinning rate better than the lipid chain length of the three phosphocholine-based ULVs of diCn:1PC with n = 18, 20, and 22.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...