Origins of possible synergistic effects in the interactions between metal atoms and MoS2/graphene heterostructures for battery applications†
Abstract
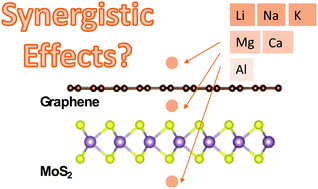
The interactions between metals and two-dimensional materials, in particular, the adsorption energies, strongly determine the performances of rechargeable batteries. Previously, it has been demonstrated that heterostructures of two dimensional (2D) materials can lead to enhanced metal adsorptions, which were ascribed to the existence of ‘synergistic’ effects amongst metal atoms and two different 2D materials. However, further investigations are still required to reveal the physical mechanisms behind the contribution of these possible ‘synergistic’ effects for metal intercalations in 2D heterostructures. Here, we selected MoS2/graphene as a prototypical system, and we examined the adsorption and intercalation thermochemistry of monovalent atoms (Li, Na and K) and multivalent atoms (Mg, Ca and Al) using density-functional theory (DFT) calculations. The synergistic effects arising from charge polarizations in these systems were quantified using the three-body interaction energy terms. Our results show strong system dependencies whereby the interactions between the Mg or Ca atom with the MoS2/graphene heterostructures might exhibit cooperative bindings. Nevertheless, metal adsorptions on top of the graphene surface were all found to be anti-cooperative in this case. Our results suggest that enhancement of metal adsorptions using 2D heterostructures is predominantly driven by increasing dispersion interactions due to increases in the interaction surface areas.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...