A quantitative methodology for the study of particle–electrode impacts†
Abstract
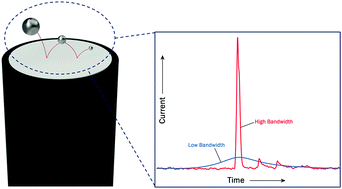
Herein we provide a generic framework for use in the acquisition and analysis of the electrochemical responses of individual nanoparticles, summarising aspects that must be considered to avoid mis-interpretation of data. Specifically, we threefold highlight the importance of the nanoparticle shape, the effect of the nanoparticle diffusion coefficient on the probability of it being observed and the influence of the used measurement bandwidth. Using the oxidation of silver nanoparticles as a model system, it is evidenced that when all of the above have been accounted for, the experimental data is consistent with being associated with the complete oxidation of the nanoparticles (50 nm diameter). The duration of many single nanoparticle events are found to be ca. milliseconds in duration over a range of experiments. Consequently, the insight that the use of lower frequency filtered data yields a more accurate description of the charge passed during a nano-event is likely widely applicable to this class of experiment; thus we report a generic methodology. Conversely, information regarding the dynamics of the nano redox event is obscured when using such lower frequency measurements; hence, both data sets are complementary and are required to provide full insight into the behaviour of the reactions at the nanoscale.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...