A novel nonlinear nano-scale wear law for metallic brake pads†
Abstract
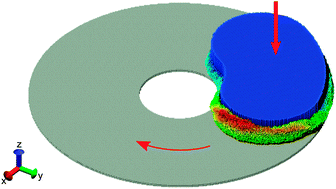
In the present work, molecular dynamics simulations were carried out to investigate the temperature distribution as well as the fundamental friction characteristics such as the coefficient of friction and wear in a disc-pad braking system. A wide range of constant velocity loadings was applied on metallic brake pads made of aluminium, copper and iron with different rotating speeds of a diamond-like carbon brake disc. The average temperature of Newtonian atoms and the coefficient of friction of the brake pad were investigated. The resulting relationship of the average temperature with the speed of the disc as well as the applied loading velocity can be described by power laws. The quantitative description of the volume lost from the brake pads was investigated, and it was found that the volume lost increases linearly with the sliding distance. Our results show that Archard's linear wear law is not applicable to a wide range of normal loads, e.g., in cases of low normal load where the wear rate was increased considerably and in cases of high load where there was a possibility of severe wear. In this work, a new formula for the brake pad wear in a disc brake assembly is proposed, which displays a power law relationship between the lost volume of the metallic brake pads per unit sliding distance and the applied normal load with an exponent of 0.62 ± 0.02. This work provides new insights into the fundamental understanding of the wear mechanism at the nano-scale leading to a new bottom-up wear law for metallic brake pads.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...