Bound and continuum-embedded states of cyanopolyyne anions†
Abstract
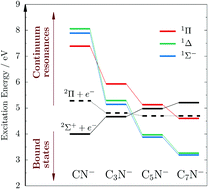
Cyanopolyyne anions were among the first anions discovered in the interstellar medium. The discovery has raised questions about the routes of formation of these anions in space. Some of the proposed mechanisms assumed that anionic excited electronic states, either metastable or weakly bound, play a key role in the formation process. The verification of this hypothesis requires detailed knowledge of the electronic states of the anions. Here we investigate the bound and continuum states of four cyanopolyyne anions, CN−, C3N−, C5N−, and C7N−, by means of ab initio calculations. We employ the equation-of-motion coupled-cluster method augmented with complex absorbing potential. We predict that already in CN−, the smallest anion in the family, there are several low-lying metastable states of both singlet and triplet spin symmetry. These states, identified as shape resonances, are located between 6.3–8.5 eV above the ground state of the anion (or 2.3–4.5 eV above the ground state of the parent radical) and have widths of a few tenths of eV up to 1 eV. We analyze the identified resonances in terms of leading molecular orbital contributions and Dyson orbitals. As the carbon chain length increases in the C2n+1N− series, these resonances gradually become stabilized and eventually turn into stable valence bound states. The trends in the energies of the transitions leading to both resonance and bound excited states can be rationalized by means of the Hückel model. Apart from valence excited states, some of the cyanopolyynes can also support dipole bound states and dipole stabilized resonances, owing to a large dipole moment of the parent radicals in the lowest 2Σ+ state.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...