Formation of new polymorphs and control of crystallization in molecular glass-formers by electric field†
Abstract
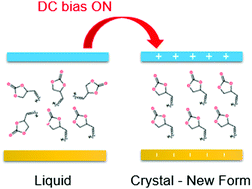
Static electric fields were observed to modify the crystallization behavior in a simple supercooled liquid, leading to a new crystal polymorph that could not be obtained in the absence of a field, even under high-pressure conditions. Using different thermal protocols and field amplitudes in the range from 40 to 200 kV cm−1, changes in both nucleation and crystal growth rates of 4-vinyl-propylene carbonate (vinyl-PC) are revealed. Remarkably, all field-induced changes in the crystallization behaviour were found to be fully reversible and do not affect dynamics of the tested liquid. Because vinyl-PC is a simple polar molecule, these field induced features are expected to occur in many other materials having permanent dipole moments. Our results highlight the important role of an external electric field as an additional control variable to influence the crystallization tendency of molecular glass-formers, and provide new opportunities in pharmaceutical science or organic electronics.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...