Ligand mediated evolution of size dependent magnetism in cobalt nanoclusters†
Abstract
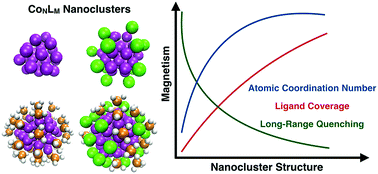
We use density functional theory to model the impact of a ligand shell on the magnetic properties of CoN (15 ≤ N ≤ 55) nanoclusters. We study three different ligand shells on each nanocluster core size, each known to have different electronic interactions with the surface: pure Cl ligand shells (X-type), pure PH3 ligand shells (L-type), and two component ligand shells with mixtures of Cl and PH3 ligands. The simulations show that the identity, arrangement, and total coverage of the ligand shell controls the distribution of local magnetic moments across the CoN core. On the surface of an unpassivated CoN nanocluster, the Co–Co coordination number (CN) is known to determine the local magnetic moments. Upon the introduction of a ligand, the Co–Co CN remains important, however the nature of the metal–ligand bond changes the extent to which increasing Co–Co CN quenches magnetism. Further, we identify an additional and significant long-range impact on local magnetic moments (LMM) from the PH3 ligand shells. Thus, we establish important design principles of magnetic nanoclusters, where ligand shell chemistry mediates the distribution of LMMs across a CoNLM nanocluster, allowing a route to rational design of specific magnetic properties.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...