Exploring the relation between the oligomeric structure and membrane damage by a study on rat islet amyloid polypeptide†
Abstract
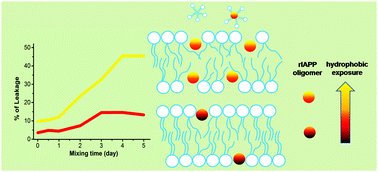
The formation of prefibrillar intermediates is a key stage not only for the fibrillation of amyloid peptides but also for their cytotoxicity. The heterogeneous and transient nature of most prefibrillar intermediates make them difficult to be separated, identified, and characterized. Rat islet amyloid polypeptide (rIAPP) has a weak propensity of fibrillation under most solution conditions and is found to be cytotoxic, which enables us to characterize prefibrillar species formed at various oligomeric states and explore the mechanism of membrane damage by these oligomers. In the present study, we prepared rIAPP oligomers under various conditions and characterized their structures, morphologies, sizes, interactions with the membrane composed of POPC/POPG 4 : 1, and disruptive efficiencies to the membrane using CD, TEM, DLS, NMR spectroscopy, and leaking assays. We found that oligomerization of rIAPP below a size limit of ∼50 nm in diameter rendered rIAPP more damaging to the membrane, whereas the formation of assemblies with sizes above this limit dramatically decreased the disruptive potency of rIAPP to the membrane. The oligomer species with smaller sizes and higher membrane-damage efficiencies have a longer time stability of α-helix at the membrane that is associated with a stronger membrane binding. Our findings show that interplay between the oligomeric size and hydrophobic exposure is implicated in the mechanism of membrane damage. The positive correlation between hydrophobic exposure and disruptive potency is valid only for the oligomers with sizes smaller than certain size limit.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...