Associative detachment (AD) paths for H and CN− in the gas-phase: astrophysical implications
Abstract
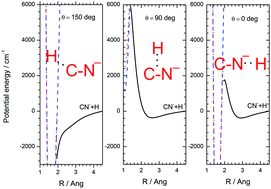
The direct dynamical paths leading to Associative Detachment (AD) in the gas-phase, and specifically in the low-temperature regions of the Dark Molecular Clouds (DMC) in the ISM, or in cold trap laboratory experiments, are investigated with quantum chemical methods by using a high-level multi-reference Configuration Interaction (CI) approach that employs single and double excitations plus Davidson perturbative correction [MRSDCI(Q)] and the d-aug-cc-pV5Z basis set. The potential energy curves for H + CN− are constructed for different directions of the H partner approaching the CN− anion within the framework of the Born–Oppenheimer approximation. The present calculations found that the AD energetics at low temperature becomes favorable only along a selected range of approaching directions, thus showing that there is a preferred path of forming HCN at low temperatures, while that of forming its HNC isomer is found to be energetically forbidden. Given the existence in the ISM of different HCN/HNC ratios in different environments, we discuss the implications of our findings for selective formation of either isomer in the low-temperature conditions of the molecular cloud cores.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Theory, experiment, and simulations in laboratory astrochemistry


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...