Synthesis of NaA zeolite membrane by maintaining pressure difference between the two sides of the support†
Abstract
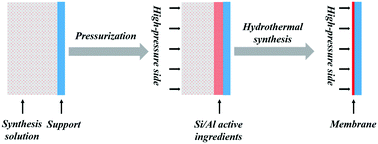
Compact and dense zeolite membranes were prepared on the inner surface of 170 mm long ceramic tubes by maintaining the pressure difference between the two sides of the support during the hydrothermal synthesis process. The effects of the pressure difference on the formation of NaA zeolite membrane were investigated in detail by X-ray diffraction spectroscopy (XRD) and scanning electron microscopy (SEM). The characterization results showed that the pressure difference created by controlling temperature or vacuum not only continuously drove fresh synthesis solution to the inner surface of the support, but also increased the binding force of the zeolite membrane to the support. However, a very large pressure difference led to a large amount of Si/Al active ingredients entering the channels of the support and blocking the pores, resulting in decrease in the permeability of the membrane. Gas permeation performance demonstrated that the pressure difference produced by controlling either the temperature or vacuum resulted in membranes with the highest permselectivities of H2 over other gases at the pressure difference of ca. 0.05 MPa between the two sides of the support. At 25 °C and 0.1 MPa, the permselectivity of H2 over N2 through the zeolite membrane synthesized by the pressure-driven method was as high as 5.21, and it was much higher than the corresponding Knudsen diffusion coefficient.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...