Internal defects-oriented dissolution: controllable evolution of hollow ZSM-5 nano-structures†
Abstract
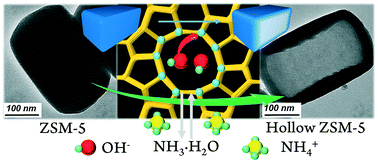
A hollow ZSM-5 nano-structure with a shell thickness of ca. 40 nm is successfully formed in 40 min via ammonia leaching under mild conditions. It is supposed to be crucial to control the release of hydroxyl ions for intact hollow structure construction. Management of the dissolution procedure enables visualization of the internal architecture, providing fundamental knowledge on the primary subunits and potential diffusion barriers of MFI-type single nanocrystals. The dissolution process can be extended to prepare hollow zeolite encapsulated catalysts with better performance in shape-selective hydrogenation reactions.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...