Multidrug salt forms of norfloxacin with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs: solubility and membrane permeability studies†
Abstract
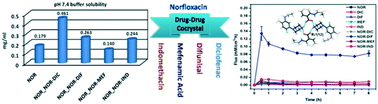
Multidrug solids have potential to efficiently treat and control a plethora of medical conditions. With the objective of discovering multidrug forms, three new multidrug salts and a salt hydrate of an antibacterial drug, norfloxacin (BCS class IV drug) with four non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs, BCS class II drugs), diclofenac (NOR–DIC), diflunisal (NOR–DIF), mefenamic acid (NOR–MEF) and indomethacin (NOR–IND–H2O), were prepared by liquid-assisted grinding. Single crystal X-ray diffraction (SCXRD) reveals that proton transfer from the carboxylic acid of the NSAIDs to the piperazinyl group of norfloxacin occurs in all the salts to form a robust tetrameric R44 (12) ring piperazine–carboxylate synthon by N+–H⋯O− bonding. Studies on the equilibrium solubility in different biological pH buffer solutions and membrane permeability have been carried out and a comparison is made with those of the parent drugs. A significant enhancement of norfloxacin solubility was observed for the pH 7.4 buffer solution in all the binary systems with the exception of the NOR–MEF salt. Also, a cumulative amount of NOR–DIF and NOR–IND–H2O binary systems show remarkable improvement in diffusion behavior compared to that of the individual pure drugs. Thus, the increasing physicochemical properties through the combined effect of improved solubility and permeability leads to the enhancement of bioavailability, which has implications that overcome the formulation-related problems of APIs.
- This article is part of the themed collection: CrystEngComm 20th volume collection


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...