Synthesis and controlled crystallization of in situ prepared poly(butylene-2,6-naphthalate) nanocomposites†
Abstract
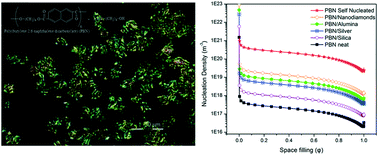
Poly(butylene-2,6-napthalate) (PBN) is a fast crystallizing engineering polyester, which can crystallize in two different modifications. Thus, besides its importance as an engineering material, PBN is treated here as a model polymer to study the effect of nanofillers on polymorphism, morphology and end-product properties. A series of novel PBN nanocomposites with silica (SiO2), silver (Ag), alumina (Al2O3) and nanodiamonds (NDs) were synthesized by in situ polymerization. The nanocomposites were crystallized in the α-crystalline form of PBN, as it was revealed by both wide-angle X-ray diffraction (WAXD) and polarized light optical microscopy (PLOM). Crystallization studies were performed under isothermal and dynamic conditions and the results showed that even though PBN is a fast-crystallizing polymer, the nanofillers were effective in increasing the crystallization rates. The PLOM images revealed that spherulitic structures prevailed at low crystallization temperatures, while dendrites were formed at higher temperatures, when crystallization was a slow process. Specific methodologies for the analysis of differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) and PLOM data are also introduced in this work, prior to the kinetic evaluation of the nucleation density and activity of fillers.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...