An in situ SERS study of ionic transport and the Joule heating effect in plasmonic nanopores†
Abstract
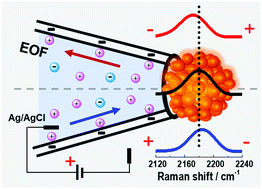
Understanding the ionic transport behaviour as well as temperature change caused by the Joule heating effect is important for the application of plasmonic nanopores. To explore the basic properties of ionic transport through nanopores, we assemble gold nanoparticles on the tip of a glass nanopipette to form a hydrophilic gold porous structure (hydro-GPS) that exhibits high Raman activity.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...