Efficient cosubstrate enzyme pairs for sequence-specific methyltransferase-directed photolabile caging of DNA†
Abstract
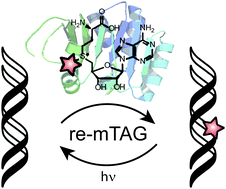
Supplemented with synthetic surrogates of their natural cosubstrate S-adenosyl-L-methione (AdoMet), methyltransferases represent a powerful toolbox for the functionalization of biomolecules. By employing novel cosubstrate derivatives in combination with protein engineering, we show that this chemo-enzymatic method can be used to introduce photolabile protecting groups into DNA even in the presence of AdoMet. This approach enables optochemical control of gene expression in a straight-forward manner and we have termed it reversible methyltransferase directed transfer of photoactivatable groups (re-mTAG).


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...