Self-assembled inorganic clusters of semiconducting quantum dots for effective solar hydrogen evolution†
Abstract
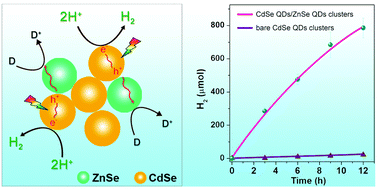
Owing to promoted electron–hole separation, the catalytic activity of semiconducting quantum dots (QDs) towards solar hydrogen (H2) production has been significantly enhanced by forming self-assembled clusters with ZnSe QDs made ex situ. Taking advantage of the favored interparticle hole transfer to ZnSe QDs, the rate of solar H2 evolution of CdSe QDs can be increased to ∼30 000 μmol h−1 g−1 with ascorbic acid as the sacrificial reagent, ∼150-fold higher than that of bare CdSe QDs clusters under the same conditions.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...