Real-time monitoring of the aggregation of Alzheimer's amyloid-β via1H magic angle spinning NMR spectroscopy†
Abstract
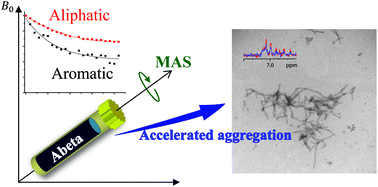
Proton magic-angle-spinning NMR used for real-time analysis of amyloid aggregation reveals that mechanical rotation of Aβ1–40 monomers increases the rate of formation of aggregates, and that the increasing lag-time with peptide concentration suggests the formation of growth-incompetent species. EGCG's ability to shift off-pathway aggregation is also demonstrated.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...