The uptake, retention and clearance of drug-loaded dendrimer nanoparticles in astrocytes – electrophysiological quantification†
Abstract
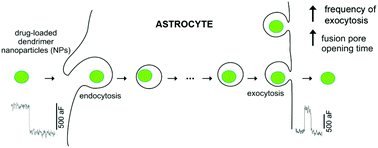
Nanoparticle-based drug delivery systems may impose risks to patients due to potential toxicity associated with a lack of clearance from cells or prolonged carrier-cell retention. This work evaluates vesicular cell uptake, retention and the possible transfer of endocytosed methylprednisolone-loaded carboxymethylchitosan/poly(amidoamine) dendrimer nanoparticles (NPs) into secretory vesicles of rat cultured astrocytes. The cells were incubated with NPs and unitary vesicle fusions/fissions with the plasma membrane were monitored employing high-resolution membrane capacitance measurements. In the NP-treated cells the frequency of unitary exocytotic events was significantly increased. The presence of NPs also induces an increase in the size of exocytotic vesicles interacting with the plasma membrane, which exhibit transient fusion with prolonged fusion pore dwell-time. Live-cell confocal imaging revealed that once NPs internalize into endocytotic compartments they remain in the cell for 7 days, although a significant proportion of these merge with secretory vesicles destined for exocytosis. Co-localization studies show the route of clearance of NPs from cells via the exocytotic pathway. These findings bring new insight into the understanding of the intracellular trafficking and biological interactions of drug-loaded dendrimer NPs targeting astrocytes.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...