A novel aptasensor based on gold nanorods/ZnS QDs-modified electrode for evaluation of streptomycin antibiotic†
Abstract
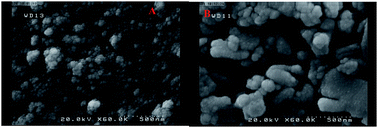
In this study, a simple and effective strategy was developed for specific detection of streptomycin (STR) antibiotic. At first, in this strategy, glassy carbon electrode (GCE) was covered by thiourea capped-ZnS QDs and gold nanorods (AuNRs) for the construction of a sensing interface for thiolated aptamer immobilization. Subsequently, the STR thiol-aptamer was covalently attached on the AuNRs/thiourea capped-ZnS QDs/GCE via Au–S bond formation. Morphology of the modified electrode was characterized via emission scanning electron microscopy (FE-SEM) technique. The proposed system showed good linearity ranging from 1 fg mL−1 to 1.111 pg mL−1 and 1.111 pg mL−1 to 11.1111 ng mL−1, with a detection limit of 0.35 fg mL−1. Furthermore, this methodology was also applied to evaluate STR in milk and serum samples, indicating the feasibility of the application of aptasensor analysis for STR detection. The presented system, in presence of different interferences, indicated good selectivity in detecting the STR. Our study provides a facile and low-cost method for designing aptamer-based sensors toward the evaluation of other antibiotics if the specific aptamer is available.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...