Comparison of the performances of several commonly used algorithms for second-order calibration
Abstract
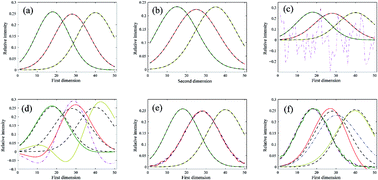
The present study compared six commonly used algorithms, namely, alternating trilinear decomposition (ATLD), self-weighted alternating trilinear decomposition (SWATLD), alternating coupled two unequal residual functions (ACTUF), parallel factor analysis (PARAFAC), damped Gauss-Newton (dGN) and algorithm combination methodology (ACM). Their performances with respect to the pre-estimated component number, convergence rate, collinearity, noise, small component and slight non-linearity (chromatographic peak drift) were considered. The results indicate that the difference in the performances of the algorithms arises from differences in the computational mode and the construction of loss functions. Among the six algorithms, ATLD, SWATLD, ACTUF and ACM were insensitive to excessive factors; the ability to overcome severe collinearity was in the order of ACM, ACTUF and dGN > SWATLD > ATLD and PARAFAC; PARAFAC, dGN and ACM showed a stronger ability to resist noise; PARAFAC was the most sensitive to a small component; and ATLD and SWATLD could overcome some effect of slight non-linearity (chromatographic peak drift). Additionally, ATLD was found to be the fastest algorithm, and dGN and ACM had faster convergence rates than PARAFAC. This study is helpful for understanding the essential difference in the performances of algorithms and can provide guidance for choosing suitable algorithms for the analysis of three-way data.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...