Maceration mediated liquid–liquid extraction of conjugated phenolics from spent black tea leaves extraction of non-extractable phenolics
Abstract
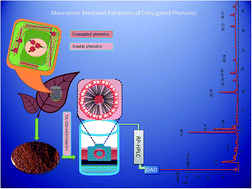
This paper puts forward the application of non-ionic surfactant based maceration to mediate the liberation of conjugated phenolics from of spent black tea leaves (SBTL). The maceration conditions including Triton X-100 concentration, temperature, solvent composition, and pH were investigated at various levels to enhance the recovery of phenolic conjugates from SBTL. The optimum conditions embracing 2.8% (w/v) TX-100, 6.9 pH, 35 °C and 75% (v/v) aqueous methanol furnished an extract equal to 34.63 ± 0.15 g/100 g SBTL containing conjugated phenolics up to 267.84 ± 1.38 milligram gallic acid equivalent per g of extract. Moreover, SBTL extracts produced through Maceration Mediated Liquid–Liquid Extraction (MMLLE) were found to be good scavengers of free radicals (IC50 2.60 ± 0.21 μg mL−1) and oxidants (135.94 ± 0.02 μM Trolox Equivalents per g of extract). RP-HPLC-DAD characterization revealed the presence of esters of gallic, chlorogenic and caffeic acids as major conjugated constituents. Overall, MMLLE was found to be an intelligent and easily scalable technique for the recovery of conjugated phenolics from SBTL.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...