Decreasing the uncertainty of peak assignments for the analysis of synthetic cathinones using multi-dimensional ultra-high performance liquid chromatography†
Abstract
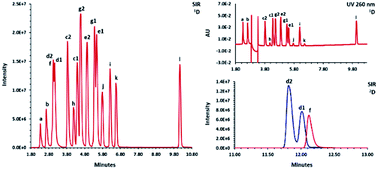
Chromatographic techniques which are commonly employed in forensic analysis utilize retention time as an identification parameter. Conventional one-dimensional chromatographic techniques such as gas and liquid chromatography inherently lack the separation power required to resolve the multitude of combinations possible when analyzing emerging drugs. Multi-dimensional chromatography, which significantly increases resolving power, is a viable means to increase the utility of retention time measurements for compound identification. This study aims to demonstrate the utility of multi-dimensional ultra-high performance liquid chromatography (UHPLC) with at-column dilution for the screening and identification of synthetic cathinones with significantly decreased uncertainty. One-dimensional separations were conducted on mixtures of 16 controlled synthetic cathinones and 7 pentedrone positional isomers in order to determine the most orthogonal combination for multi-dimensional chromatography. The separations utilized several stationary phases for both reversed phase chromatography (RPC) and hydrophilic interaction chromatography (HILIC). Based on the separations performed, it was determined that a combination of a BEH C8 column (operated in RPC mode) and an HSS PFP column (operated in HILIC mode) as the first and second dimension columns, respectively, provided orthogonal separations with a decrease in peak assignment uncertainty of at least one order of magnitude. For at-column dilution, a HILIC trapping column was used with 0.025% formic acid in acetonitrile as the loading and diluting solvent. Multi-dimensional separations conducted on early, mid, and late eluting compounds showed excellent retention time repeatability, satisfactory recovery with excellent signal-to-noise, and good peak area repeatability for both the first and second dimensions. Ten simulated samples containing various adulterants and diluents were analyzed using multi-dimensional chromatography. All 10 samples showed excellent retention time matches between the sample and its corresponding standard. Thus, multi-dimensional UHPLC would significantly reduce peak assignment uncertainty leading to increased accuracy in the identification of seized drugs.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...