Aqueous and non-aqueous electrophoresis and micellar electrokinetic capillary chromatography of a mixture of quinoline-2-thione and 8-mercaptoquinoline hydrochloride
Abstract
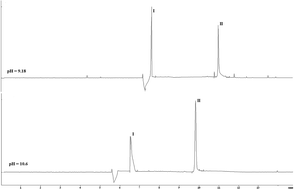
In this paper three variants of the electrophoretic method for the determination of thioamides, quinoline derivatives are given: aqueous capillary electrophoresis, micellar electrokinetic capillary chromatography and non-aqueous electrophoresis. CE has some advantages over other approaches: rapid and effective separation, relatively a simple set of tools, and a minimum amount of a sample, and the analysis time is usually short. Non-aqueous capillary electrophoresis (NACE) is an alternative technique to aqueous CE. NACE has been applied for separating some molecules under special circumstances, i.e. when analytes and electrolytes are insoluble or partially soluble in water. Micellar chromatography makes it possible to separate both ionogenic and uncharged components of the sample, due to the introduction of a surfactant into the lead electrolyte. Thus this paper reports successful separation of a mixture of compounds quinoline-2-thione (I) and 8-mercaptoquinoline hydrochloride (II) and the quantitative determination of compounds I–II by capillary zone electrophoresis (CZE) was optimized. CZE provides the sensitive and reproducible estimation of analyte concentration in the range from 0.8–161.2 μg ml−1 for quinoline-2-thione in aqueous medium and 2.19–219.2 μg ml−1 for 8-mercaptoquinoline hydrochloride in non-aqueous medium. The detection limit was 0.4 μg ml−1 for quinoline-2-thione and 1.5 μg ml−1 for 8-mercaptoquinoline hydrochloride respectively.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...