Enhanced electrochemiluminescence of luminol by an in situ silver nanoparticle-decorated graphene dot for glucose analysis†
Abstract
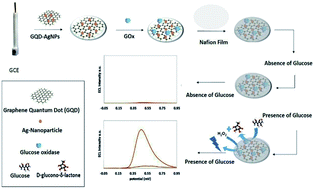
Herein, a rapid, linker-free, single-step strategy for in situ synthesis of graphene quantum dot–luminol–Ag nanoparticle (GQD–luminol–AgNP) nanocomposites was designed by reducing AgNO3 with an electrochemiluminescent reagent, luminol, in the presence of GQDs. The nanocomposites were characterized using transmission electron microscopy, UV-vis absorption spectroscopy, and EDS. The results indicated that many Ag nanoparticles (AgNPs) with an average diameter of about 5 nm were dispersed uniformly on the surface of GQD nanosheets. Luminol molecules were also decorated on the nanocomposite surface. Thus, the nanocomposites showed excellent electrochemiluminescence (ECL) activity in presence of H2O2. To build a glucose ECL-based biosensor, the prepared sensor was also modified with glucose oxidase (GOx). The GOx enzyme was covalently immobilized on the GQD–luminol–AgNP-modified glassy carbon electrode. The designed ECL biosensor showed great performance towards glucose detection in the concentration range between 25 and 250 μM with a satisfactory detection limit (8 μM).


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...