Conductometric immunoassay of alpha-fetoprotein in sera of liver cancer patients using bienzyme-functionalized nanometer-sized silica beads
Abstract
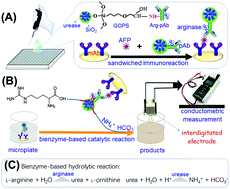
A conductometric immunoassay protocol was designed for the sensitive detection of a liver cancer biomarker, alpha-fetoprotein (AFP), in biological fluids by using enzyme-conjugated nanometer-sized enzyme-doped silica beads. Initially, urease molecules were doped into nanosilica particles by using the reverse micelle method. Thereafter, arginase-labeled anti-AFP antibodies were covalently conjugated onto the surface of the synthesized nanoparticles. The immunoreaction was carried out in a monoclonal anti-AFP capture antibody-coated microplate with a sandwich-type assay format by using bienzyme-functionalized silica nanobeads as the recognition elements. Upon L-arginine introduction, the substrate was cleaved into urea and L-ornithine on the basis of the arginase enzymatic reaction, and the as-produced urea was then decomposed into ammonia (NH4+) and bicarbonate (HCO3−) ions by the doped urease, thus causing the variation in the local conductivity of the detection solution on an interdigitated conductometric transducer. Under optimal conditions, the developed immunosensing system exhibited good conductometric responses toward target AFP within a dynamic linear range of 0.01–100 ng mL−1 at a relatively low detection limit of 4.8 pg mL−1 based on the 3sB criterion. Importantly, good reproducibility, high specificity and acceptable method accuracy were acquired for the analysis of human serum specimens in liver cancer patients.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...