Electrochemical detection of Alzheimer's disease related substances in biofluids by silica nanochannel membrane modified glassy carbon electrodes†
Abstract
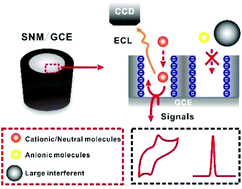
Alzheimer's disease (AD) affects middle- and old-age populations, and causes loss of brain weight, degradation of brain functions and memory loss. So the fast and accurate detection of AD related markers is highly important in diagnosis. We report in this work the detection of Cu2+ and dopamine (DA), which are markers related to AD, by direct electrochemistry (DEC) and electrochemiluminescence (ECL) using a silica nanochannel membrane modified glassy carbon electrode (SNM/GCE). By DEC, the detection of both Cu2+ and DA in buffer solutions was achieved with a wide linear range and a low limit of detection (LOD). The determination of DA was also achieved in terms of its quenching effect on the ECL of the tris(2,2′-bipyridyl)ruthenium(II)/tri-n-propylamine co-reactant system in both intensity and image modes, yielding a particularly high sensitivity in the former case. In comparison with a bare GCE, the analytical sensitivity and selectivity of the SNM/GCE were superior, most likely due to the analyte pre-concentration and permselective effects of the SNM. Moreover, given that the SNM consists of perpendicular channels with a negatively charged surface, high channel density (ca. 7.5 × 1012 cm−2) and uniform size (ca. 2.3 nm in diameter), it displays a high molecular permeability and meanwhile a high selectivity in terms of molecular size and charge. So the SNM/GCE exhibited an excellent anti-fouling ability in biofluids, such as human blood and artificial cerebrospinal fluid, suppressing effectively the interference of coexisting substances (such as cells, proteins, and other big and small molecules) and providing excellent signal stability.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...