Near-infrared broadband cavity-enhanced sensor system for methane detection using a wavelet-denoising assisted Fourier-transform spectrometer
Abstract
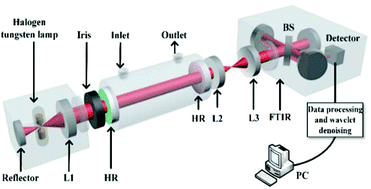
The majority of broadband cavity-enhanced systems are used to detect trace gas species in the visible spectral range. We demonstrated a broadband cavity-enhanced sensor system in combination with a Fourier-transform spectrometer (FTS) in the near-infrared (near-IR) region for methane (CH4) detection. Light from a tungsten–halogen lamp was coupled into a high-finesse cavity and the light leaking from the cavity was imaged onto the FTS. An optimal incident beam diameter of 2.25 cm was required in the condition of a 40 cm-long cavity of a 2.5 cm diameter and a 100 cm radius of curvature (RoC) mirror. The CH4 sensor system was capable of operating at a temperature of 300 K and 1 atm gas pressure. Based on an Allan variance analysis, a minimum detectable absorption coefficient of 4.6 × 10−7 cm−1 was achieved. A wavelet denoising (WD) method was introduced in the retrieval of the gas concentration, which improved the measurement precision from 10.2 parts-per-million in volume (ppmv) to 5.3 ppmv with an enhancement factor of 2 for a 20 min averaging time. The near-IR broadband cavity-enhanced sensor system can also be used to measure high-resolution absorption spectra of other atmospheric trace gas species.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...
