Ion mobility mass spectrometry provides novel insights into the expression and structure of gangliosides in the normal adult human hippocampus
Abstract
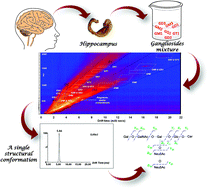
Clustered into the so-called “glycosynaptic” microdomains in the central nervous system (CNS), gangliosides (GGs) are involved in the formation of functional synapses and neural circuits. Therefore, GGs are important biomarkers in the early diagnosis of CNS pathologies, which are the focus of our research as potential therapeutic targets. A series of neuropsychiatric disorders, including Alzheimer's disease and schizophrenia, are characterized by amnesia and disorientation caused by hippocampal atrophy and diminished cholinergic activity. Based on ion mobility mass spectrometry (IM-MS) capability for the reliable determination of glycopatterns, the changes in the diversity and number of GGs with age and the occurrence of neurological disorders, we report here the development of a high performance IM-MS strategy for assessing the GG profile in a complex mixture extracted from a 20 year old hippocampus. IM separation of GGs based on the charge state, carbohydrate chain length and degree of sialylation led to the detection and identification of 140 species, the largest number of GGs ever reported in an adult hippocampus. Moreover, the obtained data support the concept of GG cholinergic activity. IM tandem MS experiments using collision induced dissociation (CID) confirmed the incidence of GD1b(d18:1/24:1) in the investigated hippocampus specimen.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...