Development of a selective and highly sensitive fluorescence assay for nucleoside triphosphate diphosphohydrolase1 (NTPDase1, CD39)†
Abstract
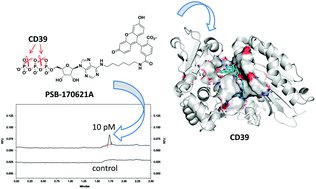
Ecto-nucleoside triphosphate diphosphohydrolase1 (NTPDase1, CD39) is a major ectonucleotidase that hydrolyzes proinflammatory ATP via ADP to AMP, which is subsequently converted by ecto-5′-nucleotidase (CD73) to immunosuppressive adenosine. Activation of CD39 has potential for treating inflammatory diseases, while inhibition was suggested as a novel strategy for the immunotherapy of cancer. In the present study, we developed a selective and highly sensitive capillary electrophoresis (CE) assay using a novel fluorescent CD39 substrate, a fluorescein-labelled ATP (PSB-170621A) that is converted to its AMP derivative. To accelerate the assays, a two-directional (forward and reverse) CE system was implemented using 96-well plates, which is suitable for the screening of compound libraries (Z′-factor: 0.7). The detection limits for the forward and reverse operation were 11.7 and 2.00 pM, respectively, indicating a large enhancement in sensitivity as compared to previous methods (e.g. malachite-green assay: 1 000 000-fold, CE-UV assay: 500 000-fold, fluorescence polarization immunoassay: 12 500-fold). Enzyme kinetic studies at human CD39 revealed a Km value of 19.6 μM, and a kcat value of 119 × 10−3 s−1 for PSB-170621A, which shows similar substrate properties as ATP (11.4 μM and 82.5 × 10−3 s−1). The compound displayed similar properties at rat and mouse CD39. Subsequent docking studies into a homology model of human CD39 revealed a hydrophobic pocket that accommodates the fluorescein tag. PSB-170621A was found to be preferably hydrolyzed by CD39 as compared to other ectonucleotidases. The new assay was validated by performing inhibition assays with several standard CD39 inhibitors yielding results that were consonant with data using the natural substrates.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Analyst Recent HOT articles


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...