Mapping phosphate modifications of substituted lipid A via a targeted MS3 CID/UVPD strategy†
Abstract
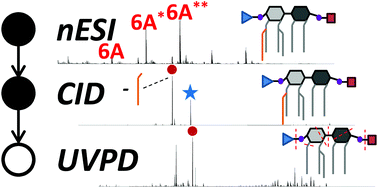
Structural characterization of lipid A from Gram-negative bacteria remains a significant challenge, especially with respect to localizing modifications of the phosphate groups typically found on the reducing and non-reducing ends of the β-1′,6-linked glucosamine disaccharide backbone of lipid A. As reported here, combining traditional collisional activated dissociation (CAD) and ultraviolet photodissociation (UVPD) in a hybrid MS3 approach facilitates identification and localization of substituents of the phosphate groups. The focus is on rapid identification and characterization of substituted lipid A species with specific emphasis on the modifications on the 1 and 4′ phosphate moieties. Mapping these modifications, typically ones that modify the surface charges of lipopolysaccharides, is particularly important owing to the impact of these types of modifications on antibiotic resistance. The presence of phosphoethanolamine, aminoarabinose, and galactosamine moieties in hexaacylated and heptaacylated lipid A species, including ones from Enterobacter cloacae and Acinetobacter baumannii, are characterized using a targeted MS3 strategy to identify glycosidic product ions (1,5X1 and 0,4A2, typically) which allow localization of the substituents.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...