Colorimetric sensor for cimetidine detection in human urine based on d-xylose protected gold nanoparticles†
Abstract
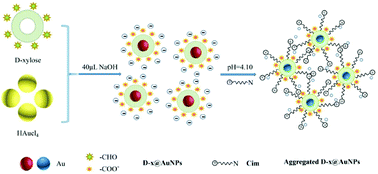
Herein, a simple, novel, and rapid colorimetric sensor for cimetidine (Cim) detection based on D-xylose protected gold nanoparticles (D-x@AuNPs) has been developed for the first time. The D-x@AuNPs were characterized by UV-vis, TEM and FT-IR techniques. Cimetidine causes the aggregation of D-x@AuNPs due to the formation of a strong covalent Au–N bond and electrostatic binding. As the cimetidine concentration increased, the color of the solutions gradually changed from wine-red to blue, and the large absorption band shifted from 533 to 680 nm upon D-x@AuNP aggregation. The effects of different experimental parameters were investigated. A comparative study on the detection of Cim using citrated capped AuNPs and D-x@AuNPs was presented. Under optimum conditions, the UV-vis spectra showed that the absorption ratio (A680/A533) increased linearly with the concentration of cimetidine in the range of 7 × 10−8 to 3 × 10−6 M with a correlation coefficient of 0.9956 and a limit of detection of 1 × 10−8 M without needing any complicated instruments. The selectivity of the D-x@AuNP detection system for cimetidine was excellent when compared with other ions and analytes. Due to their rapid and visible color changes, and their remarkable selectivity, the D-x@AuNPs synthesized in this study were suitable and could be applied to the detection of cimetidine in human urine.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...