Metal–organic frameworks as affinity agents to enhance the microdialysis sampling efficiency of fatty acids†
Abstract
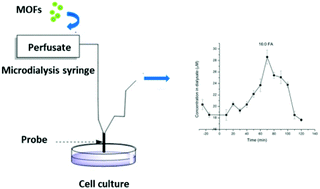
Microdialysis (MD) has been extensively used for in vivo sampling of hydrophilic analytes such as neurotransmitters and drug metabolites. In contrast, there have been few reports on sampling of lipophilic analytes by MD. Lipophilic analytes are easily adsorbed on the surfaces of the dialysis membrane and the inner wall of tubing, which leads to a very low relative recovery (RR). In this work, a strategy to develop an enhanced MD sampling of fatty acids (FAs) by using metal–organic frameworks (MOFs) as affinity agents in the perfusion fluid was investigated. Two MOFs, MIL-101 and ZIF-8, were synthesized and tested for the first time. A 2 times higher RR, about 70% RR, was obtained. The FT-IR experiment showed that the unsaturated metal sites in MOFs could coordinate with FAs, therefore the FAs were encapsulated into MOFs, avoiding FAs to be absorbed on the surfaces of the dialysis membrane and the inner wall of tubing. Moreover, incorporation of FAs into MOFs led to a decrease of free concentration of FAs inside the MD membrane and an increase of concentration gradient, allowing more FAs to diffuse across the membrane. Consequentially, an enhanced RR was obtained. The approach was successfully used to monitor the time profile of targeted FAs in cell culture media after lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced inflammation.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...