A highly sensitive and wide-range pressure sensor based on a carbon nanocoil network fabricated by an electrophoretic method†
Abstract
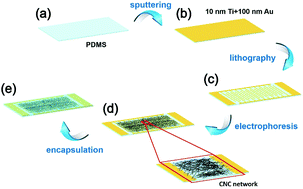
A highly sensitive and wide-range pressure sensor based on a carbon nanocoil (CNC) network fabricated by an electrophoretic method was fabricated and studied. The pressure sensor can withstand a maximum pressure of 100 kPa and maintain a high sensitivity of more than 150 kPa−1 when the pressure is more than 50 kPa. It is worth noting that the sensor exhibited an ultrahigh sensitivity of 193 kPa at the pressure of 70 kPa. A high stability and reproducibility of more than 10 000 loading–unloading cycles and a rapid response time of approximately 48 ms were achieved. The pressure sensor can clearly distinguish the minimum pressure of 0.5 kPa. This study also presents a concept of the optimal value, which can be used to evaluate the performances of different types of pressure sensors. The optimal value of this sensor is up to 3.72 × 106, which is 300 times higher than that of most of the current pressure sensors. Practically, the pressure sensor shows an excellent performance in detection of finger tapping, air pressure, and vibration, exhibiting a great potential in the applications of vibration detection devices and pressure detection equipment because of its ultrahigh sensitivity and pressure resistance.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...