Spectroscopic and electrical signatures of acceptor states in solution processed Cu2ZnSn(S,Se)4 solar cells†‡
Abstract
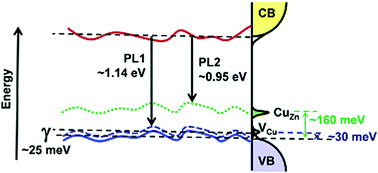
The nature and dynamics of acceptor states in solution-processed Cu2ZnSn(S,Se)4 (CZTSSe) thin films are investigated by variable temperature photoluminescence (PL) and electrical impedance spectroscopy. Highly pure I-4 phase CZTSSe with the composition Cu1.6ZnSn0.9(S0.23Se0.77)4 is synthesized by sequentially spin coating of dimethyl-formamide/isopropanol solutions containing metal salts and thiourea onto Mo coated glass, followed by annealing in an Se atmosphere at 540 °C. As-annealed films are highly compact with a thickness of 1.3 μm and grain sizes above 800 nm, with a band gap of 1.18 eV. Photovoltaic devices of 0.25 cm2 with the architecture glass/Mo/CZTSSe/CdS/i-ZnO/Al:ZnO demonstrate a power conversion efficiency reaching up to 5.7% in the absence of an anti-reflective coating. Under AM 1.5G illumination at 296 K, the best device shows a 396 mV open-circuit voltage (VOC), 27.8 mA cm−2 short-circuit current (JSC) and 52% fill factor (FF). The overall dispersion of these parameters is under 15% for a total of 20 devices. In the near IR region, PL spectra are dominated by two broad and asymmetrical bands at 1.14 eV (PL1) and 0.95 eV (PL2) with characteristic power and temperature dependences. Analysis of the device electrical impedance spectra also reveals two electron acceptor states with the same activation energy as those observed by PL. This allows assigning PL1 as a radiative recombination at localized copper vacancies (VCu), while PL2 is associated with CuZn antisites, broadened by potential fluctuations (band tails). The impact of these states on device performance as well as other parameters, such as barrier collection heights introduced by partial selenization of the back contact, are discussed.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...