Formation of arsenene p–n junctions via organic molecular adsorption†
Abstract
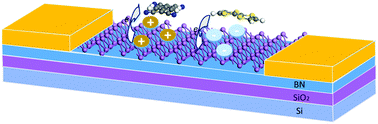
Arsenene-based device applications such as transistors and photodetectors benefit from precise control over the carrier type and concentration as well as a combination of both high-quality p-doped and n-doped components to form p–n junctions. Here, it is demonstrated using first-principles calculations that selective organic molecular adsorption allows us to effectively control the carrier type in arsenene. Moreover, upon applying an in-plane tensile strain, the carrier concentration effectively increases. Furthermore, the BN substrate can increase the structural stability without any impact on the doping character of the arsenene sheet. This opens the possibility of creating arsenene p–n junctions.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...