The role of oxygen in dramatically enhancing the electrical properties of solution-processed Zn–Sn–O thin-film transistors†
Abstract
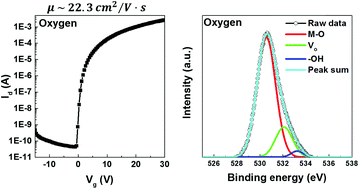
The mechanism of formation of metal–oxide–metal (M–O–M) bonds in solution-processed metal oxide semiconductors can vary depending on the types of precursors used. To date, metal-alkoxides or metal-chloride precursors have mainly been studied; therefore, efforts to improve the device characteristics of oxide thin-film transistors (TFTs) have been limited to these types of precursors. On the other hand, systematic studies to optimize the experimental conditions (e.g. thickness and annealing atmosphere) of oxide TFTs made by using new types of precursors have rarely been reported. In this study, we successfully demonstrate high-performance solution-processed Zn–Sn–O TFTs by using a metal-carboxylate precursor, tin(II) 2-ethylhexanoate, and optimizing the oxide thickness and thermal annealing conditions. To determine the optimum thickness of Zn–Sn–O, we prepared 3 types of active layers with different thickness combinations of ZnO and SnO2. In addition, we found that oxygen gas in the annealing process maximizes the formation of M–O–M bonds and decreases the number of trap sites in the thickness-optimized active layer, leading to dramatically enhanced device performances. As a result, the optimized Zn–Sn–O TFTs based on tin(II) 2-ethylhexanoate exhibit excellent mobility exceeding 22 cm2 V−1 s−1, which is an order of magnitude higher than that of the previously reported Zn–Sn–O TFTs based on the same precursor and very comparable to the mobility levels obtained from conventional solution-processed metal-oxide TFTs. We believe that our approach will enrich the current family of tin precursors and provide another option for resource-friendly, low-cost, and high performance Zn–Sn–O semiconductors.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...