An embedded-PVA@Ag nanofiber network for ultra-smooth, high performance transparent conducting electrodes†
Abstract
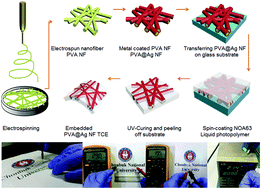
Flexible transparent conducting electrodes (TCEs) in replacement of brittle indium tin oxide (ITO) films are of ultimate importance in the production of flexible and stretchable displays, lighting devices, and solar panels with the ability to resist harsh weather conditions. Herein, the fabrication of an ultra-smooth, highly flexible transparent conducting electrode with a fully embedded structure of the silver coated electrospun polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) nanofiber (PVA@Ag NF) network is reported. These electrodes are fabricated using a scalable electrospinning and thermal evaporation process. The embedded PVA@Ag NF (E-PVA@Ag NF) network TCE structure provides several advantages, including a smooth surface, mechanical stability under high bending stress, and strong adhesion to the substrate with excellent flexibility, without sacrificing the electrical–optical properties. Ultrahigh aspect ratios with fused crossing at the junction points of the PVA@Ag NF network result in a high transmittance (∼90%) at a low sheet resistance (∼2.56 Ω □−1). The E-PVA@Ag NF network TCE structure shows a smooth surface topology (RRMS ∼ 2.0 nm) with excellent bending stability; the sheet resistance of the TCE remains almost constant after 10 000 bending cycles with a 1.0 mm bending radius. Finally, a flexible transparent heater is fabricated and its performance at low operating voltage is reported.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...