Nondestructive up-conversion readout in Er/Yb co-doped Na0.5Bi2.5Nb2O9-based optical storage materials for optical data storage device applications†
Abstract
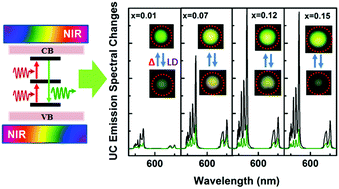
Luminescence modulation based on photochromic reactions is always considered to be a promising method to achieve nondestructive readout in photochromic materials. Generally speaking, two conventional strategies have been widely used to achieve this target: tuning the absorption bands and adjusting luminescent quenching mechanisms. In this paper, we found a new strategy to improve effectively luminescence readout capability in Er/Yb codoped NBN-based solid-state inorganic photochromics by using a two-photon absorption mode of luminescent centers. Upon alternating visible light irradiation (407 nm) and the thermal stimulus, the materials exhibited a high luminescence switching contrast ratio (ΔRt = 86%), excellent reversibility, and significantly improved luminescent efficiency (22 times). Most importantly, the photochromic reaction process can be efficiently read out using the two-photon absorption (or up-conversion) mode without inducing any new reactions, showing extremely low destruction on information recording (destruction degree <11%), which is superior to other luminescence emission modes (down-shifting or down-conversion). These results could be used as a guide to tailor the luminescence modulation properties of photochromic materials to realize non-destructive readout in 3D optical data storage device applications.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...