Preparation of novel anionic polymeric ionic liquid materials and their potential application to protein adsorption†
Abstract
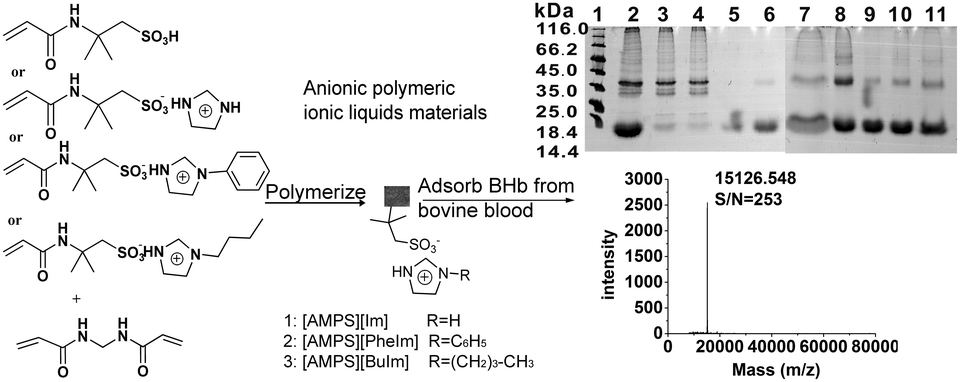
A series of anionic polymeric ionic liquid (PIL) materials with high adsorption capacities toward proteins were developed using a 2-acrylamido-2-methylpropane sulfonic acid imidazole derivative ([AMPS][RIm]) (R: –H, –C6H5, or –(CH2)3CH3) as the functional monomer. An anionic polymeric ionic liquid monomer (ILM) containing imidazole cations modified with alkyl derivatives (butyl or phenyl groups) and sulfonic group-functionalized anions was chosen as the only monomer to prepare materials for protein adsorption. The resultant anionic PIL materials were characterized by scanning electron microscopy, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, differential scanning calorimetry, and thermogravimetric analysis. The adsorption behaviors of the obtained anionic PIL materials toward proteins was evaluated. The results indicated that the anionic PILs material showed superior adsorption for different proteins at different pH values: ovotransferrin (OVT, 861.5 mg g−1) and bovine serum albumin (BSA, 842.2 mg g−1) at pH 4.0; bovine hemoglobin (BHb, 983.4 mg g−1) and cytochrome c (Cytc, 882.9 mg g−1) at pH 7.0; and casein (605.2 mg g−1) at pH 8.0. The feasibility of the resultant material for separating BHb from real bovine blood has also been demonstrated. The convenient preparation of anionic PIL materials and ultra-high adsorption capacity toward proteins predicted its attractive and potential broad applications in proteomics, medical diagnosis, and sensors.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...