Multi-arm star-branched polymer as an efficient contrast agent for tumor-targeted magnetic resonance imaging†
Abstract
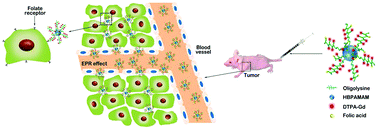
Contrast agents with high efficiency and safety are excellent candidates as magnetic resonance imaging probes. Herein, a multi-arm star-branched polymer was prepared by conjugating oligolysine onto a rigid hyperbranched poly(amido amine) core via click chemistry, followed by covalent modification with Gd chelate and folic acid (FA-OLL-g-HBPAMAM-DTPA-Gd). This multi-arm star-branched polymer contrast agent exhibited much higher longitudinal relaxivity (r1 = 13.34 mM−1 s−1) as compared to a commercial contrast agent (Gd-DTPA, r1 = 4.2 mM−1 s−1). No obvious histological toxicity was observed from histological assessment, which illustrated that FA-OLL-g-HBPAMAM-DTPA-Gd exhibited excellent biocompatibility. Both in vitro and in vivo MRI studies showed that the macromolecular contrast agent provided better signal contrast enhancement and presented obvious target specificity to KB xenografts with a sufficient time window for MRI scanning; moreover, this multi-arm star-branched mCA has great potential for developing sensitive and biocompatible MRI CA with targeting ability.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...