Injectable hydrogel-incorporated cancer cell-specific cisplatin releasing nanogels for targeted drug delivery
Abstract
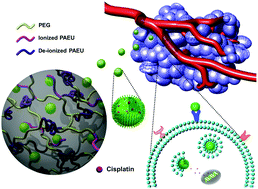
Cisplatin (CDDP) is a well-known anticancer agent, and it has been widely used to treat various solid tumors during clinical cancer therapy. Nevertheless, therapeutic applications of CDDP are hampered by its severe side effects. Although CDDP can be encapsulated into nano-scale drug delivery formulations to improve its physicochemical properties, the lack of stability in the formulation and cancer cell-specific targetability have prompted the exploration of novel vectors for the targeted delivery of CDDP. Here, we introduce CDDP-bearing chondroitin sulfate nanogels (CS-nanogels) that are synthesized through a chelating ligand–metal coordination cross-linking reaction, and then incorporated into pH- and temperature-responsive bioresorbable poly(ethylene glycol)–poly(β-aminoester urethane) (PEG–PAEU) hydrogels for cancer cell-specific delivery of CDDP. The CS-nanogels released from the hydrogels exhibit a pH-dependent release of CDDP. CDDP was released slowly under physiological conditions (pH 7.4), whereas the release of CDDP was triggered under acidic conditions (pH 5.0). Confocal microscopy images demonstrated that fluorescein-5-thiosemicarbazide-labeled CS-nanogels released from the hydrogels selectively bound to the A549 lung carcinoma cell line through the overexpressing CD44 receptor but not to NIH 3T3 cells. An in vitro cytotoxicity test indicated that CS-nanogels released from the hydrogels effectively inhibited the growth of A549 lung carcinoma cells. Subcutaneous injection of CS-nanogel-loaded PEG–PAEU copolymer sols into the dorsal region of Sprague-Dawley rats spontaneously formed a viscoelastic gel without causing noticeable inflammation at the injection site and was found to be bioresorbable in eight weeks. Overall, the injectable hydrogel-incorporated CS-nanogels were demonstrated to be a useful formulation for the targeted delivery of CDDP.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...