MgAl-layered double hydroxide nanoparticles co-delivering siIDO and Trp2 peptide effectively reduce IDO expression and induce cytotoxic T-lymphocyte responses against melanoma tumor in mice†
Abstract
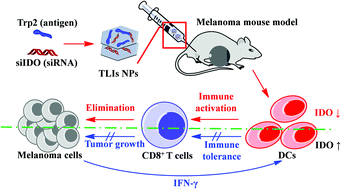
Active immunotherapy has shown promising potential for cancer treatment. However, there still remain major challenges including induction of a potent and specific T-cell response against the endogenous antigen and retention of tumor immunity. To address these problems, we used layered double hydroxide (LDH) nanoparticles (NPs) to co-deliver tyrosinase-related protein 2 (Trp2) and indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase siRNA (siIDO) to dendritic cells (DCs). These LDH NPs were readily taken in by DCs, and escaped from endosomes into the cytoplasm. Compared with free Trp2 peptide or siIDO, the vaccination with the LDH NPs co-delivering Trp2 and siIDO significantly inhibited tumor growth in melanoma mouse models by relieving IDO-mediated immune suppression and increasing naïve and specific T cell activation process in vivo. Thus, these LDH NPs, which have a high loading capacity for peptide or siRNA effectively protect and deliver Trp2 and siIDO, overcome the immune tolerance and strengthen T cell immunity, are potential therapeutics to enhance cancer treatment.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...