A colloidally stable water dispersion of Ni nanowires as an efficient T2-MRI contrast agent†
Abstract
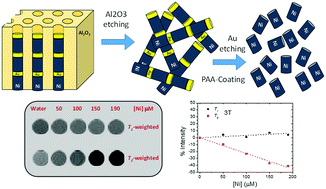
A colloidally stable dispersion of anisotropic Ni nanowires in water has been achieved showing good performance as a T2-contrast agent in magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). A wet chemistry approach has been developed that renders water dispersible Ni nanowires of controlled size. Firstly, an array of Ni/Au multilayer nanowires of tailored dimensions was synthesized by pulsed electrodeposition within a porous alumina template in a three-electrode cell at room-temperature. Then, Ni/Au multilayer nanowires were released from the template followed by the isolation of the Ni segments through a two-step acidic etching, ending up with a colloidally stable dispersion of poly-acrylic acid (PAA)-coated Ni nanowires in water solution. The PAA-coated Ni nanowires have been morphologically and structurally characterized by scanning and transmission electron microscopy (SEM, TEM, respectively), whereas their ferromagnetic properties were studied using a SQUID-magnetometer. Importantly, relaxivity properties (transversal relaxivity, r2) indicated good performance of PAA-coated Ni nanowires as a T2-contrast agent at 1.41 T and body temperature, with values as large as those of commercial contrast agents based on iron oxide nanoparticles. MRI phantom imaging at clinical fields of 3 T confirmed the dark contrast effect of PAA-coated Ni nanowires, as compared to a water control, which opens a new window of opportunities for anisotropic metal nanostructures as contrast agents in MRI applications.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...