An intracellular temperature nanoprobe based on biosynthesized fluorescent copper nanoclusters†
Abstract
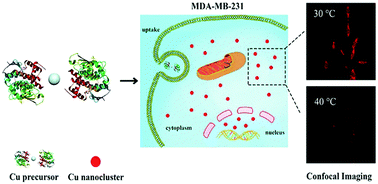
Temperature variation is related to a series of biological reactions and abnormal medical processes of living cells. Fluorescence-based temperature nanoprobes have great potential for cellular imaging and temperature measurement. In this study, we have established a facile, efficient and green strategy for the preparation of an intracellular temperature nanoprobe specifically by in situ biosynthesized fluorescent copper nanoclusters (CuNCs). Our observations demonstrate that the fluorescent CuNCs could specifically be biosynthesized spontaneously in MDA-MB-231 cancer cells through a particular molecular process, but not in normal cells (i.e., L02 cells). The resultant CuNCs, with an average diameter of 2.4 ± 0.4 nm, were found to exhibit red fluorescence emission (λem = 610 nm) and could further efficiently accumulate for bioimaging in target cancer cells. More importantly, the fluorescence signal of the biosynthesized CuNCs is sensitively thermo-responsive over the physiological temperature range in MDA-MB-231 cells (relative sensitivity: −3.18% per Celsius). This provides an efficient nanothermometer based on the in situ biosynthesized CuNCs for cellular fluorescence imaging and other biomedical applications.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...