Fetal nucleated red blood cell analysis for non-invasive prenatal diagnostics using a nanostructure microchip
Abstract
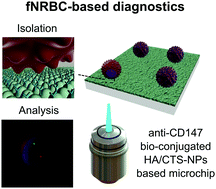
Cell-free DNA has been widely used in non-invasive prenatal diagnostics (NIPD) nowadays. Compared to these incomplete and multi-source DNA fragments, fetal nucleated red blood cells (fNRBCs), once as an aided biomarker to monitor potential fetal pathological conditions, have re-attracted research interest in NIPD because of their definite fetal source and the total genetic information contained in the nuclei. Isolating these fetal cells from maternal peripheral blood and subsequent cell-based bio-analysis make maximal genetic diagnosis possible, while causing minimal harm to the fetus or its mother. In this paper, an affinity microchip is reported which uses hydroxyapatite/chitosan nanoparticles as well as immuno-agent anti-CD147 to effectively isolate fNRBCs from maternal peripheral blood, and on-chip biomedical analysis was demonstrated as a proof of concept for NIPD based on fNRBCs. Tens of fNRBCs can be isolated from 1 mL of peripheral blood (almost 25 mL−1 in average) from normal pregnant women (from the 10th to 30th gestational week). The diagnostic application of fNRBCs for fetal chromosome disorders (Trisomy 13 and 21) was also demonstrated. Our method offers effective isolation and accurate analysis of fNRBCs to implement comprehensive NIPD and to enhance insights into fetal cell development.
 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...